Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the injured newborn brain
We focus on brain injury in the neonatal period which is a major contributor to mortality and morbidity in the newborn. In our translational research group we study how early life events, like hypoxic-ischemic perinatal events, including birth asphyxia and perinatal stroke, or (extreme) preterm birth, lead to injury in the developing brain and how this impacts neurodevelopmental outcome on the long run.
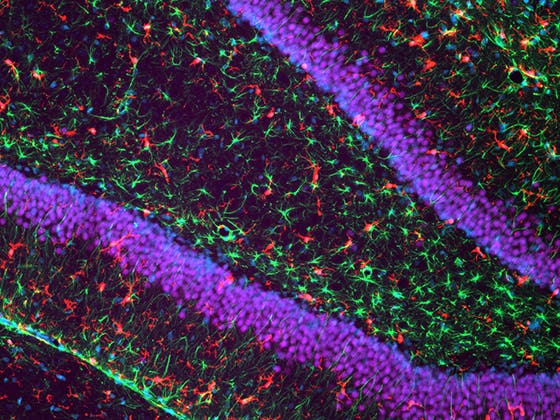
Brain of a rat exposed to fetal inflammation and postnatal hypoxia as a model for encephalopathy of prematurity, showing active microglia (red, Iba-1) and astrocytes (green, GFAP) in the hippocampus (neuronal nuclei in blue). Courtesy of Chantal Kosmeijer.
Our team explores the pathophysiological cellular and molecular mechanisms of early brain injury in in vitro and in vivo models relevant for the target patient. In one of our research lines we try to decipher early damaging cascades after hypoxic-ischemic injury in the term brain. Understanding the intricate interplay between these detrimental cascades can aid in identifying novel targets to develop new strategies to combat neuronal brain injury in the newborn brain. We currently focus on targets within neuronal apoptotic cascades, mitochondrial key proteins and neuroinflammatory routes.
Fixed rat pup brain ready for embedment in paraffin. Courtesy of Judit Alhama Riba & Sebastiaan Corstjens.
In an additional research line, we focus on developing models for brain injury after extreme preterm birth (i.e. encephalopathy of prematurity (EoP)) including cerebral organoids. We study the underlying pathophysiology of EoP which comprises of hypomyelination of the developing brain, maturational arrest of oligodendrocyte precursors, aberrant interneuron development and neuroinflammation. We currently investigate whether stem cell therapy, growth factor supplementation (see also “Regenerative strategies for the injured neonatal brain”), human milk oligosaccharide supplementation (see also “Nutraceuticals for the developing brain”) or immunomodulation would be promising strategies to boost myelination in the preterm brain.
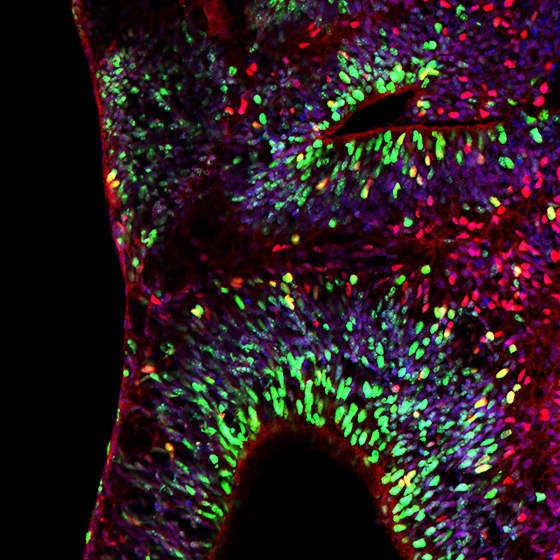
Cerebral organoid stained for proliferating cells (red, Ki67) and oligodendrocytes (green, Olig2), DAPI is used as nuclear counterstain. Courtesy of Myrna Brandt.
Our research laboratory is located in the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital.
Key publications uitklapper, klik om te openen
- Van Tilborg E, Achterberg EJM, van Kammen CM, van der Toorn A, Groenendaal F, Dijkhuizen RM, Heijnen CJ, Vanderschuren LJMJ, Benders MNJL, Nijboer CH. Combined fetal inflammation and postnatal hypoxia causes myelin deficits and autism-like behavior in a rat model of diffuse white matter injury. Glia 2018; 66:78-93.
- Van Tilborg E, Heijnen CJ, Benders MJ, van Bel F, Fleiss B, Gressens P, Nijboer CH. Impaired oligodendrocyte maturation in preterm infants: potential therapeutic targets. Progress Neurobiol. 2016; 136:28-49.
- Nijboer CH, Bonestroo HJC, Zijlstra J, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ. Mitochondrial JNK phosphorylation as a novel therapeutic target to inhibit neuroinflammation and apoptosis after neonatal ischemic brain damage. Neurobiol Dis. 2013; 54:432-444.
- Nijboer CH, Heijnen CJ, van der Kooij MA, Zijlstra J, van Velthoven CT, Culmsee C, van Bel F, Hagberg H, Kavelaars A. Targeting the p53 pathway to protect the neonatal ischemic brain. Ann Neurol. 2011; 70(2):255-64.
- Nijboer CH, Heijnen CJ, Groenendaal F, May MJ, van Bel F, Kavelaars A. Strong neuroprotection by inhibition of NF-kappaB after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia involves apoptotic mechanisms but is independent of cytokines. Stroke. 2008; 39(7):2129-37.
Funding & Grants uitklapper, klik om te openen
- 3V stimuleringsfonds (2020): Organoïde-model voor hersenschade bij te vroeg geboren kinderen (Myrna Brandt)
- ZonMw Meer Kennis, Minder Dieren (2018): Witte stof hersenschade in neonatale ratten leidt niet tot verminderde cognitieve vaardigheden op volwassen leeftijd (Erik van Tilborg)
- Brain Foundation the Netherlands (2016), the Next Step program: Intranasal growth factor treatment: a novel strategy to repair the injured preterm brain
- Brain Foundation the Netherlands (2014), fellowship: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy to repair white matter injury in the preterm neonatal brain: boosting oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination
- WKZ Research Funding (2013): A novel strategy to protect the preterm brain against perinatal white matter injury
- ZonMw Meer Kennis, Minder Dieren (2023): Timing of fetal exposure to inflammation steers developmental brain injury in the newborn rat
In the media uitklapper, klik om te openen
- In Dutch: Hersenmagazine (april 2021): Repareren van hersenschade na vroeggeboorte
- In Dutch: Springer Link (2008): Nieuwe therapie bij zuurstofgebrek in hersenen
- In Dutch: Instantie voor Dierenwelzijn Utrecht: 3V-Stimuleringsfonds: een organoïde van het te vroeg geboren brein
Contact uitklapper, klik om te openen
PI's: Cora Nijboer and Caroline de Theije
Dr. Cora Nijboer, personal profile page
Email: C.Nijboer@umcutrecht.nl
LinkedIn page, Cora on Twitter
Dr. Caroline de Theije, personal profile page
Email: C.G.M.deTheije@umcutrecht.nl
LinkedIn page
