Regenerative strategies for the injured neonatal brain
We focus on brain injury in the neonatal period which is a major contributor to mortality and morbidity in the newborn.
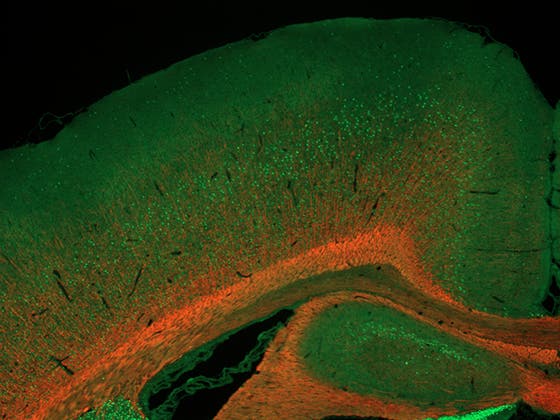
Will MSC treatment boost myelination (red, MBP) in brains of rats exposed to fetal growth restriction as a model for encephalopathy of prematurity? Deep cortical layers are stained for CTIP2 (green). Courtesy of Judit Alhama Riba.
Current treatments to combat hypoxic-ischemic brain injury or encephalopathy of prematurity (i.e. brain injury due to extreme preterm birth) are very scarce. Therefore we are dedicated to develop new therapeutic neuroprotective and neuroregenerative strategies to improve outcome for these smallest of patients. We take a true bench-to-bedside approach by using clinically relevant cell- and animal-models to closely mimic brain injury in the human newborn and to test new treatment options via clinically applicable routes. We work in close collaboration with the clinical Department of Neonatology.
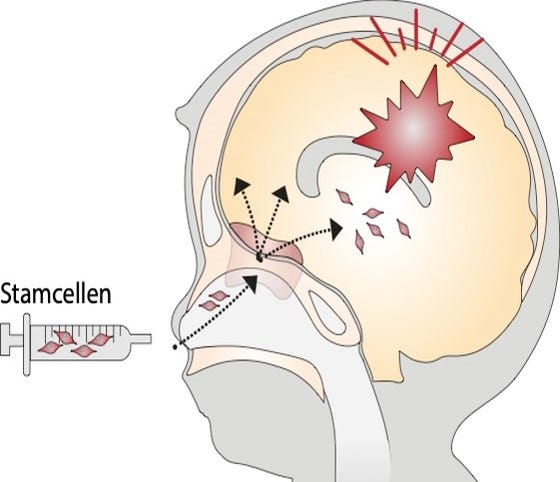
Illustration of intranasal application of mesenchymal stem cells to support endogenous neuroregeneration after neonatal brain injury.
At present, one of our key focus points is developing intranasal mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy from bench-to-bedside for neonatal brain injury. We study the migration of MSCs from the nose into damaged brain lesions, we focus on optimization strategies for cell-based therapy, and we explore mechanisms of neurorepair and stimulation of endogenous stem cell niches. Our previous research in this field has led to the first-in-human clinical trial in which safety of intranasal MSC application in term neonates with perinatal stroke has been explored (PASSIoN). We are currently also developing this therapy for encephalopathy of prematurity in animal models for fetal inflammation and fetal growth restriction.
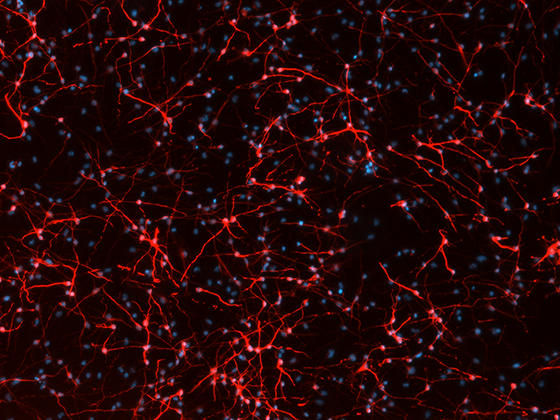
Differentiation of neural stem cells into neuronal networks (red, betaIII-tubulin) in vitro is stimulated by mesenchymal stem cell-secreted factors. DAPI as nuclear counterstain. Courtesy of Sara De Palma.
Besides MSCs, we also explore the use of neural stem cells and the use of crucial growth factors like IGF1 as regenerative strategies to improve neurodevelopment after neonatal brain injury. Furthermore, we are aiming for combination therapies with stem cells and nutrition (see also the research line Nutraceuticals for the developing brain).
Our research laboratory is located in the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital.
Key publications uitklapper, klik om te openen
- Baak LM, Wagenaar N, van der Aa NE, Groenendaal F, Dudink J, Tataranno ML, Mahamuud U, Verhage CH, Eijsermans RMJC, Smit LS, Jellema RK, de Haan TR, ter Horst HJ, de Boode WP, Steggerda SJ, Prins HJ, de Haar CG, de Vries LS, van Bel F, Heijnen CJ, Nijboer CH, Benders MJNL. Feasibility and safety of intranasally administered mesenchymal stromal cells after perinatal arterial ischaemic stroke in the Netherlands (PASSIoN): a first-in-human, open-label intervention study. Lancet Neurology 2022; 21:528-536.
- Vaes JEG, Kosmeijer CM, Kaal M, van Vliet R, Brandt MJV, Benders MJNL, Nijboer CH. Regenerative Therapies to Restore Interneuron Disturbances in Experimental Models of Encephalopathy of Prematurity. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 22(1): 211.
- Vaes JEG, van Kammen CM, Trayford C, van der Toorn A, Ruhwedel T, Benders MJNL, Dijkhuizen RM, Möbius W, van Rijt SH, Nijboer CH. Intranasal mesenchymal stem cell therapy to boost myelination after encephalopathy of prematurity. Glia. 2021; 69(3):655-680.
- Vaes JEG, Brandt MJV, Wanders N, Benders MJNL, de Theije CGM, Gressens P, Nijboer CH. The impact of trophic and immunomodulatory factors on oligodendrocyte maturation: Potential treatments for encephalopathy of prematurity. Glia. 2021; 69(6):1311-1340.
- Donega V, Nijboer CH, van Tilborg G, Dijkhuizen RM, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ. Intranasally administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2014; 261:53-64.
Funding & grants uitklapper, klik om te openen
- ZonMw Vici (2023): NEOREPAIR: unravelling the cellular and molecular mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-driven repair in the injured newborn brain
- Dr. C.J. Vaillant Fund (2021): Stamceltherapie om Zenuwnetwerken te Herstellen bij Pasgeborenen
- EU (H2020) (2020): PREMSTEM: Brain injury in the premature born infant: stem cell regeneration research network
- EU (Marie Sklodowska-Curie COFUND) RESCUE project (2018): Development of novel protective and regenerative treatment strategies for brain injury in the preterm and fullterm neonate.
- WKZ Research Fund (2017): Advances in cell-based therapy for the injured newborn brain: Optimizing nurture, habitat and momentum of mesenchymal stem cells
- Brain Foundation the Netherlands (2016), the Next Step program: Intranasal growth factor treatment: a novel strategy to repair the injured preterm brain
- Brain Foundation the Netherlands (2014), fellowship: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy to repair white matter injury in the preterm neonatal brain: boosting oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination
- NWO (ZonMw TAS) (2011): Adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) to regenerate the neonatal brain
In the media uitklapper, klik om te openen
- February 2023 - University Utrecht: Seven Utrecht-based researchers receive Vici grant
- May 2022 - NPO1 (in Dutch): Cora Nijboer, Manon Benders en Sebastiaan Mennes over een nieuw wondermiddel voor baby's.
- May 2022 - Volkskrant (in Dutch): Veelbelovend onderzoek: baby's hebben na beroerte baat bij stamcellen via de neus.
- April 2022- New Scientist (in Dutch): We hebben de stamcel de laatste tien jaar echt omarmd.
- November 2021 - Utrecht University: How stem cell therapy can repair brain injuries in newborns.
- January 2020 - RTV Utrecht (in Dutch): Miljoenensubsidie UMC Utrecht onderzoek vroeggeboren baby's.
Contact uitklapper, klik om te openen
PI's: Cora Nijboer and Caroline de Theije
Dr. Cora Nijboer, personal profile page
Email: C.Nijboer@umcutrecht.nl
LinkedIn page, Cora on Twitter
Dr. Caroline de Theije, personal profile page
Email: C.G.M.deTheije@umcutrecht.nl
LinkedIn page
